
Salman Khan
I'm a computer vision researcher affiliated with MBZUAI and ANU.
Twitter
G. Scholar
LinkedIn
E-Mail
Research Projects
Life-long Learning
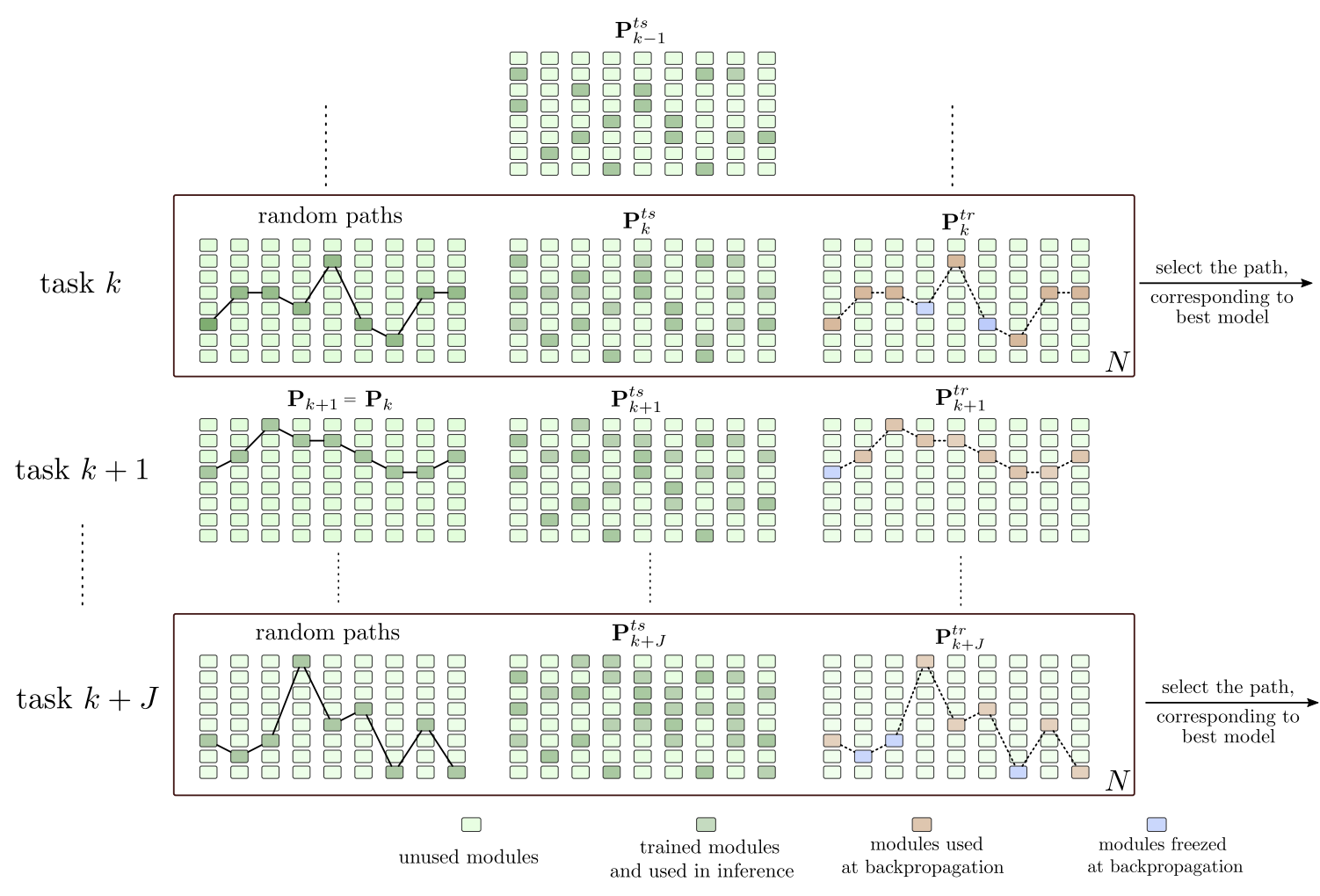 |
The ability to incrementally learn novel tasks and acquire new knowledge is necessary for life-long
machine learning. Deep neural networks suffer from ‘catastrophic forgetting’, a phenomenon
that occurs when a network is sequentially trained on a series of tasks and the learning acquired
on new tasks interferes with the previously learned concepts. As an example, in a typical transfer
learning scenario, when a model pre-trained on a source task is adapted to another task by fine-tuning
its weights, its performance significantly degrades on the source task whose weights are overridden
by the newly learned parameters. It is, therefore, necessary to develop continual learning models
capable of incrementally adding newly available classes without the need to retrain models from
scratch using all previous class-sets (a cumulative setting).
|
Multi-modal and Multi-task Foundational Models
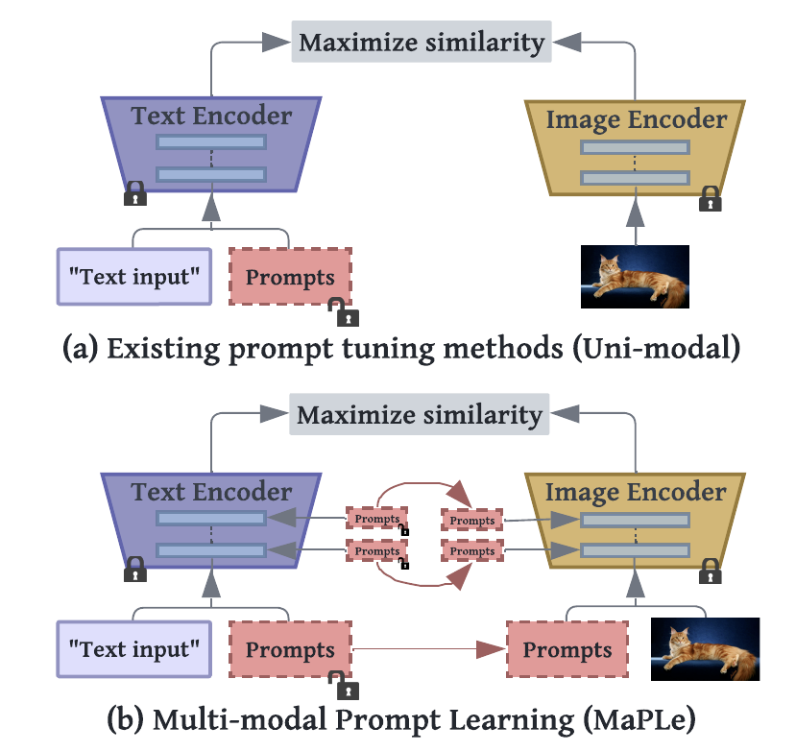 |
Pre-trained vision-language (V-L) foundational models such as CLIP have shown excellent generalization ability to downstream tasks.
However, their quick adaptation for downstream tasks and novel modalities pose challenges.
As an example, they are sensitive to the choice of input text prompts and require careful selection of prompt templates to perform well.
Inspired by the Natural Language Processing (NLP) literature, recent CLIP adaptation approaches learn prompts as the textual inputs to
fine-tune CLIP for downstream tasks. We note that using prompting to adapt representations in a single branch of
CLIP (language or vision) is sub-optimal since it does not allow the flexibility to dynamically adjust both representation
spaces on a downstream task. We have been working on multi-modal prompt learning as a quick adaptation strategy for foundational models.
In parallel, developing and adaptation of foundational models for diverse modalities e.g., videos and remote sensing is also a main
focus of this research stream.
|
Limited Supervision Object Detection
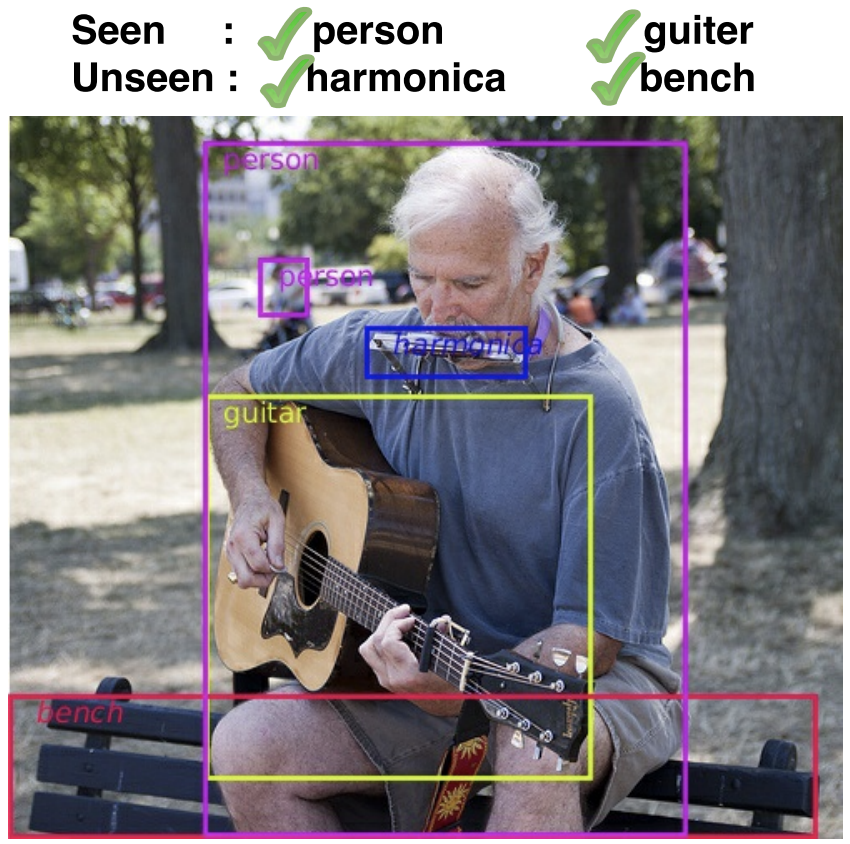 |
Since its inception, zero/few-shot learning research has been dominated by the object classification problem.
Although it still remains as a challenging task, the recognition setting has a number of limitations
that render it less suitable for real-life scenarios. First, the recognition setting is destined to work
for simpler cases where only a single dominant object is present. Second, the attributes and
semantic descriptions are relevant to individual objects instead of the entire scene composition.
Third, zero/few-shot recognition provides an answer to unseen or rare categories in elementary tasks,
e.g., classification and retrieval, yet it is unable to scale to advanced tasks such as scene
interpretation and contextual modeling, which require a fundamental reasoning about all salient objects. This
research theme seeks to address these challenges in an object detection framework.
|
All-in-one Image Restoration
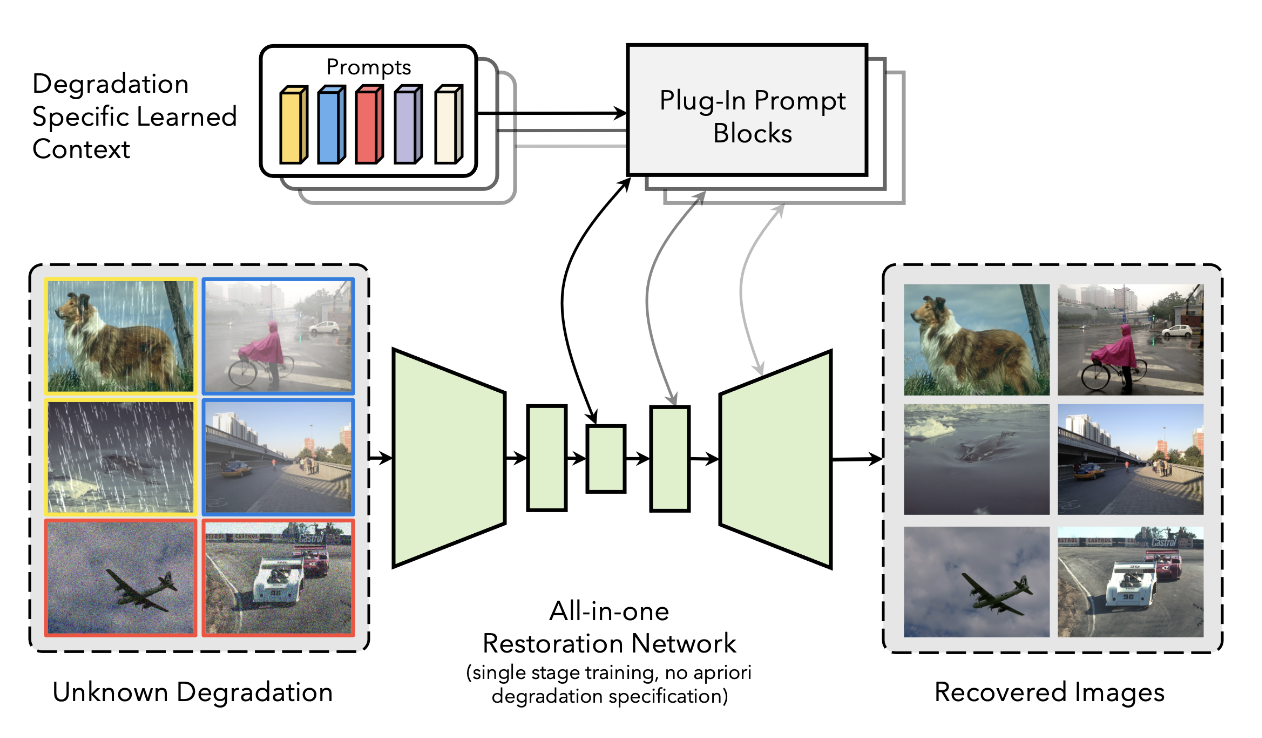 |
Image restoration involves recovering a high-quality clean image from its degraded version. Deep learning-based
methods (including seminal contributions from our lab such as MPRnet, MIRnet, Restormer, and BIPnet) have
significantly improved image restoration performance, however, they have limited generalization
ability to different degradation types and levels. This restricts their real-world application since it requires
training individual models for each specific degradation and knowing the input degradation type to apply the
relevant model. In this project, we aim at various All-In-One image restoration methods, including a
prompt-based learning approach, PromptIR, that can effectively restore images from various types and
levels of degradation. PromptIR offers a generic and
efficient plugin module with few lightweight prompts that can be used to restore images of various types and
levels of degradation with no prior information on the corruptions present in the image.
|
Adversarial Attacks and Defenses
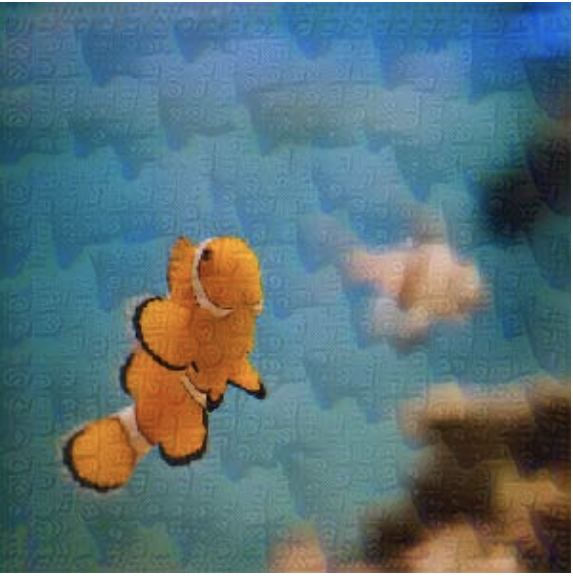 |
Adversarial examples contain small, human imperceptible perturbations specifically designed by an adversary to
fool a learned model. These examples pose a serious threat for security critical applications, e.g.
autonomous cars, bio-metric identification and surveillance systems. Furthermore, if a slight perturbation
added to a benign input drastically changes the deep network’s output with a high-confidence, it reflects
that our current models are not distinctively learning the fundamental visual concepts.
Therefore, the study of various adversarial attacks and the design of robust deep networks goes a
long way towards developing reliable and trustworthy artificial intelligence systems.
|
Spectral Representations
 |
Spectral signatures of natural scenes were earlier found to be distinctive for different scene types with varying spatial
envelope properties such as openness, naturalness, ruggedness, and symmetry. Recently, such handcrafted features
have been outclassed by deep learning-based representations. This project focuses on the development of novel spectral descriptions of
convolution features, implemented efficiently as a unitary transformation within deep network architectures.
We show that the spectral transformation decorrelates convolutional activations, which reduces co-adaptation between feature detections, thus acts as an
effective regularizer.
|
Change Detection
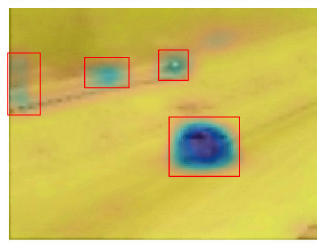 |
This project relates to the automatic detection of changes in visual imagery. First, we address the problem of weakly
supervised change detection in a pair of color images. Our structured deep learning based approach requires only image-level labels to
simultaneously detect and localize changes. Second, we address the forest change detection problem using satellite imagery.
Our proposed approach is capable of performing change analysis at a much finer temporal resolution by recovering the missing information
and automatically learns strong features from the raw surface reflectance data.
|
Scene Categorization
 |
This project addresses the challenging problem of scene categorization where diverse intra-class variations and confusing inter-class
similarities exist. We develop two novel solutions to solve this problem. First, a new approach is developed which exploits rich mid-level
convolutional features in a transformed domain to categorize indoor scenes. The feature represenatation not only incorporates the discriminative
aspects of the target dataset, but it also encodes the features in terms of the general object categories that are present in indoor scenes.
Second, we propose a new learnable feature descriptor to handle large scale deformations caused by spatial layout and scale variations in
indoor scenes.
|
Geometry Estimation
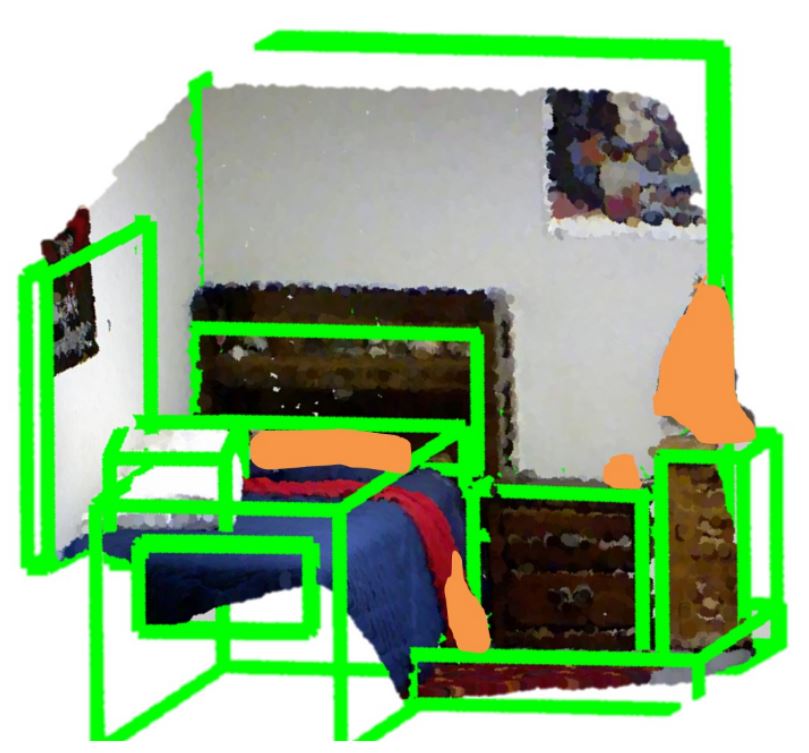 |
Objects' spatial layout estimation and clutter identification are two important tasks to understand indoor scenes.
We propose to solve both of these problems in a joint framework using RGBD images of indoor scenes. In contrast to recent
approaches which focus on eitherone of these two problems, we perform `fine grainedstructure categorization' by
predicting all the major objects and simultaneously labeling the cluttered regions. A conditional random field model
is proposed to incorporate a rich set of local appearance, geometric featuresand interactions between the scene elements.
|
Semantic Labelling
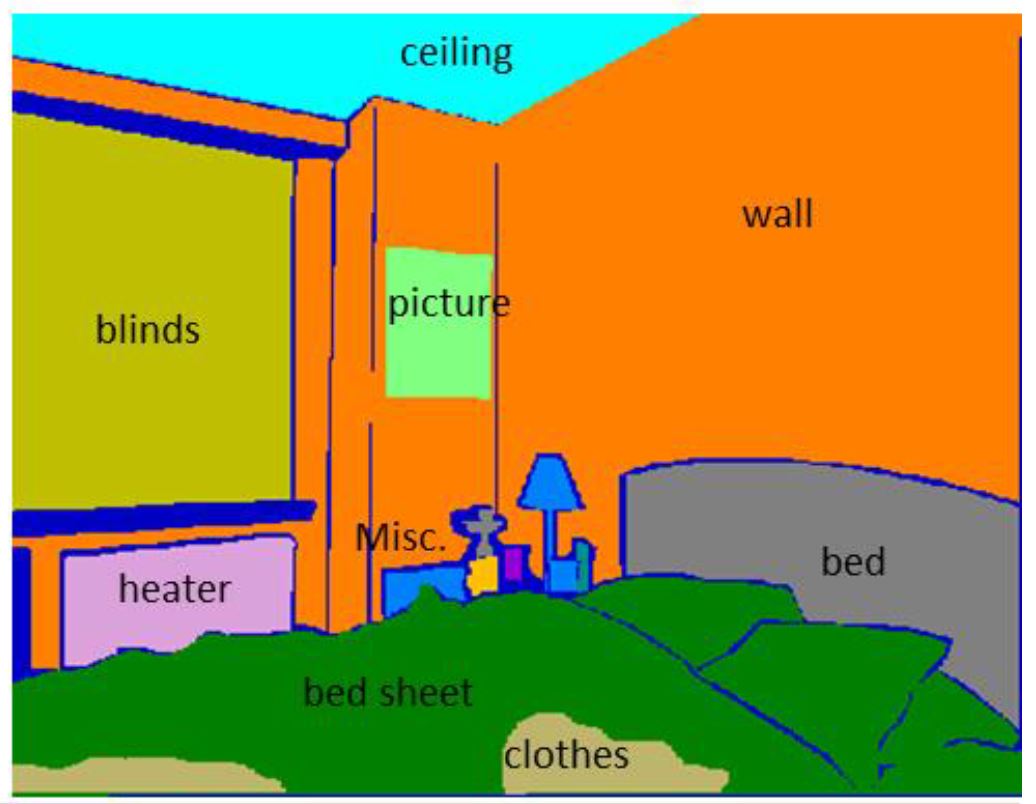 |
Inexpensive structured light sensors can capture rich information from indoor scenes, and scene labeling problems
provide a compelling opportunity to make use of this information. In this work, we present a novel Conditional Random Field (CRF)
model to effectively utilize depth information for semantic labeling of indoor scenes. At the core of the model, we propose a
novel and efficient plane detection algorithm which is robust to erroneous depth maps. Our CRF formulation defines
local, pairwise and higher order interactions between image pixels.
|
Shadow Detection and Removal
 |
We present a framework to automatically detect and remove shadows in real world scenes from a single image. Previous works
on shadow detection put a lot of effort in designing shadow variant and invariant hand-crafted features. In contrast, our
framework automatically learns the most relevant features in a supervised manner using multiple convolutional deep neural
networks (ConvNets). Using the detected shadow masks, we propose a Bayesian formulation to accurately extract shadow matte and
subsequently remove shadows. The Bayesian formulationis based on a novel model which accurately models the shadow generation
process in the umbra and penumbra regions.
|
Signature Verification
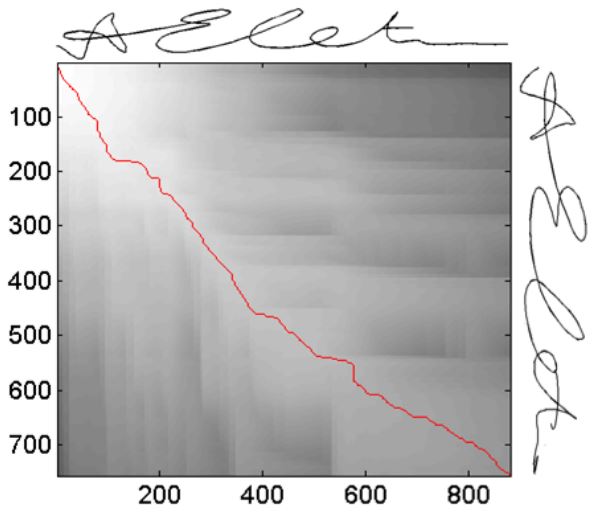 |
Handwritten signatures are one of the most socially acceptable and traditionally used person identification and
authentication metric. Although a number of authentication systems based on handwritten signatures have been proposed, a little
attention is paid towards employing signatures for person identification. In this work, we address both the identification and
verification problems related to analysis of dynamic handwritten signatures. In this way, the need to present user name before
biometric verification can be eliminated in current signature based biometric authentication systems. A compressed sensing
approach is used for user identification and to reject a query signature that does not belong to any user in the database.
|
Template Security
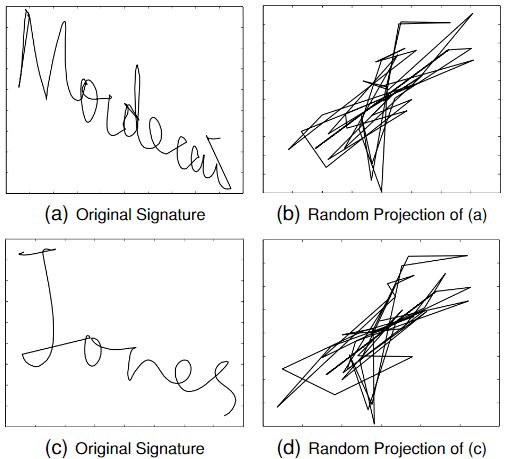 |
Exposure of unprotected authentication data is a high risk threat for organizations with online presence. The challenge is:
how to ensure security of multi-factor authentication data without deteriorating the performance of an identity verification system?
To solve this problem, we present a novel framework that applies random projections to biometric data (inherence factor), using secure
keys derived frompasswords (knowledge factor), to generate inherently secure, e�cient and revocable/renewable biometric templates for
users’ verification. We evaluate the security strength of the framework against possible attacks by adversaries.
|